Teeth and Mouth
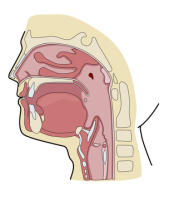 The Mouth
The Mouth
The mouth and teeth are very interesting parts of the human anatomy. For instance, the tongue is the body's most flexible muscle. The mouth and teeth are also the first step in breaking down food. When a person chews food, the food is shredded and ground. Strong muscles move the lower jaw (or mandible) while the food is being chewed. Front teeth cut the food while the back teeth grind the food.
When food is being chewed saliva is secreted into the mouth. Saliva helps to soften food and contains an enzyme which helps to break down the starch in the food.
The soft tissue in the mouth (gingiva) is more commonly known as the gums and covers the bone which holds the teeth in place. The gums surround the teeth and cover the jawbone, creating a protective barrier.
Other parts of the mouth include:
- The tongue - A muscular organ that performs several different functions. The tongue is attached to the bottom of the mouth by a membrane called the lingual frenum. The top of the tongue contains papillae, which are the tiny bumps that include the taste buds. One of the tongue's functions is tasting, but it also aids in chewing, swallowing, digesting and speaking. The tongue guides food to the teeth so it can be properly swallowed and then digested. The tongue is also very important in speech, as it works with the teeth to form certain speech patterns.
- The palate - The palate, or the roof of the mouth, is separated into two parts: the soft palate and the hard palate. The hard palate is the solid, immovable part of the mouth that attaches to the gums and teeth, forming an arch. The soft palate, which is located behind the hard palate toward the back of the throat, is the flexible area of the mouth where the gag reflex occurs.
- The cheeks - The cheeks form the sides of the mouth and continue along the front of the face to the person's lips. They are composed of subcutaneous fat, with the outside layer covered by skin and the inside being composed of a mucous membrane. The cheek muscles, also called buccinators, are important in acts such as swallowing, smiling, compression and retaining food in the mouth for chewing and digestion.
- The lips - The lips are composed of soft and pliable fleshy tissue that connects to the front of the cheeks. The outside of the lips is covered by skin. The gums attach to the part of the lips inside the mouth that is covered by the mucous membrane. Lips are red because of their blood vessels, which are close to the surface. Lips are the most mobile of all the organs in the body. Lips aid in speech but also help keep food between the teeth. Lips also allow suckling during infancy. The lips are extremely sensitive and have many receptors to help determine the texture and temperature of food.
- The floor of the mouth - This area consists largely of the tongue. It is made up of mucous membranes that extend inward from both sides of the lower jawbone and from the tongue to the gumline, which forms a crescent shape. The floor of the mouth also contains glands, portions of the muscles of the tongue and nerves.
The Teeth
Humans have four types of teeth, each of which plays a different role. Incisors, located at the front of the mouth, are chisel-shaped and have sharp edges for cutting food. Canines are pointed and known as eye teeth. They are designed for tearing food. The premolars, which have two ridges, and the flatter molars, which are the strongest and largest teeth, grind and crush food.
The part of the tooth above the gum is called the crown, while the root of the tooth is embedded in the jawbone. Where these two parts meet (at the gum or gingival surface) is the neck of the tooth. The outer part of the crown is made of enamel which is bone-like. It is also the hardest substance in the body. Lying beneath this is a layer of softer but very strong tissue called dentin, which absorbs shocks. The center of the tooth contains a soft dental pulp which contains nerves and blood vessels. Below the gum lies bone-like cementum. Periodontal ligament tissues secure the tooth in the jawbone.
Adults typically have on each side of their jaw two incisors, one canine, two premolars and three molars. This is a total of 32 teeth. However, some people have certain teeth which never erupt or grow out of the gum. This is particularly true for the four rearmost molars, which are also called "wisdom teeth." Wisdom teeth are frequently extracted in order to prevent displacement of the other teeth.
Teeth can become sensitive when the enamel on the surface wears out or the gums recede to expose the nerve fibers to the external environment. Hypersensitivity signals the fact that the dentin is exposed and the pulp has become vulnerable to damage.
Teeth can also become sensitive due to attrition and abrasion. Attrition is the loss of teeth structure due to mechanical forces from opposing teeth. Attrition first affects the enamel, but if left unchecked, can proceed to the underlying dentin. Once it is past the enamel, attrition destroys dentin quickly and gradually affects the whole tooth.
Wearing of the enamel can also be caused by abrasion, which can be caused by the use of hard toothbrushes, floss, toothpicks or any other dental appliances. This type of wear generally affects the junction between the tooth and the gum. The teeth most often affected due to abrasion are premolars and canines.
A few facts to consider regarding teeth include:
- Teeth are alive, like bones. They begin forming before an individual is born and continue to develop until adulthood.
- Most children have about 20 teeth by the time they are 3 years old.
- Permanent teeth are just beneath the roots of the baby teeth.
- Growth of the permanent tooth causes the root of the baby tooth to dissolve, and the baby tooth falls out.
Posted in Teeth & Mouth
Ask a Question Or Join a DiscussionTeeth and Mouth Disorders
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a gum disease that happens when the tissue (or gingiva) that supports the teeth gets inflamed and infected. When the gingiva becomes infected, the gums become red and swollen, and tend to bleed when the individual with gingivitis brushes their teeth. However, gingivitis is easily treated and with good oral hygiene may be cured. If gingivitis remains untreated, however, it becomes what is called periodontitis. Periodontitis is when the gum infection spreads to the ligaments that hold the teeth to the jawbone, and even the jawbone itself. The ligament infection causes the gums to separate from the teeth, and can lead to tooth loss. Indeed, periodontitis is actually the most common cause of tooth loss.
Mouth Ulcers
Prevention of mouth ulcers starts with strong oral hygiene, including brushing twice per day, flossing daily, and going to the dentist on a regular basis. The dentist should also file down jagged teeth and replacing any ill-fitting dental appliances, so as to avoid cutting an individual’s mouth in any way. Other tips to prevent mouth ulcers include avoiding the ingestion of tobacco products like cigarette or chewing tobacco, and getting a good night’s sleep on a regular basis.
Dry Mouth
This condition is caused by an inadequate flow of saliva, leaving the mouth uncomfortably parched. Dry mouth is merely a symptom due to several possible underlying illnesses. This condition can also be a side effect from taking various medications or undergoing different medical treatments.
Toothache
The most common causes of a toothache include dental decay, an abscess, inflammation of the pulp in the tooth, a damaged tooth or an exposed tooth root or irritation following a dental examination or treatment.



