Boils
 Overview
Overview
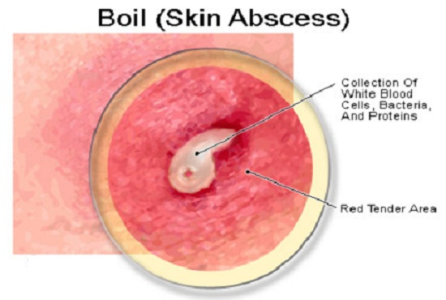
An inflamed lump under the surface of the skin as the result of a skin infection is known as a boil. Boils begin as a painful, red lump that swells and fills with pus, eventually hardening to form a yellow head.
Boils can be very tender and cause emotional distress, particularly if the boil is noticeable. This condition usually occurs on the neck, face, back, buttocks, armpits or groin area but can also occur on other areas of the body.
Symptoms of Boils
This condition can produce several symptoms, including the following:
- A lump under the surface of the skin that is hard and sore
- Soreness in the general area around the lump
- Fever
- Swollen glands
- Infected hair follicle
- Enlarged lymph glands
- Infected sebaceous gland
- Impaired resistance to infection
- Constipation
- Feeling rundown or in general not healthy
- Diabetes
Causes
Boils are caused by bacteria which enters the skin. They can also result from other conditions such as scabies and eczema. Some individuals are prone to frequent infections. Boils are contagious and can spread if someone comes in contact with an infected person.
Recurrent boils may be seen in people who have decreased immune systems, diabetes, underactive thyroid, chronic gastrointestinal problems, borderline nutrient deficiencies, or even chronic emotional stress.
Prevention of Boils
This condition can be caused by fungus, bacteria, a virus, a chemical irritation or physical trauma to the skin. Typically the cause is bacterial, with the culprit being either staphylococcus or streptococcus, both of which live on the skin. They are more prominent in people with diabetes or with weakened immune systems, those who have poor hygiene or are obese, or people who perspire a lot or wear clothing that is extremely tight.
Boils can be prevented by improving hygiene, losing weight, and wearing looser clothing. It is also helpful to eliminate possible chemical irritants.
Treatments for Boils
The boil may recur until the sac surrounding the pus (called the "core") is expelled. A physician may prescribe a topical drying paste containing magnesium sulphate, an antiseptic with benzoyl peroxide, or an antibiotic such as mupirocin. When an oral antibiotic is in order, penicillin or cyclosporine are usually the first choices for common boils. A herpetic boil which is caused by herpes simplex virus is typically treated with acyclovir. If the boil is caused by a fungus instead of bacteria, the boil is treated with a topical antifungal ointment such as econazole.
Natural Treatments
Of course, a healthy diet is required for anyone combatting an illness or infection. Eat plenty of multi-colored vegetables in order to provide the body with all the nutrients and phytochemicals necessary to strengthen the immune system. Avoid any foods that can depress the immune system, including junk food, hydrogenated oils and trans-fatty acids, and simple carbohydrates and sugars. Foods which an individual may be allergic to or intolerant of, such as dairy, wheat and corn, should also be eliminated.
A three-day detox can be undertaken to help eliminate impurities, reduce inflammation and provide the nutrients needed to boost the immune system. This juice "fast" should mainly consist of green vegetables and carrots. Celery and cucumbers are also very good for juicing because their high water content yields lots of juice.
Herbs and spices that enhance the immune system can be added to foods. Choose those that have antiseptic properties, such as ginger and garlic. Also, 4 ml of burdock root as a tincture or 500 mg in capsule form can be taken to detoxify the skin. Goldenseal in a 500 mg capsule is beneficial for its anti-inflammatory and immune-enhancing properties.
Drink lots of water. Water guards against dehydration and flushes toxins out of the body. Under normal conditions, five large glasses of water per day should be consumed, but when a disturbance is present on the skin, drinking even more water should be a priority. Drinking large quantities of water supports the actions of the kidneys and helps to guard against headaches and constipation.
Natural remedies that can be used when suffering from boils include:
- Belladonna - When this substance is taken early, it can stop the boil from further development or move it to the next stage where pus is formed. Take belladonna at the first sign of a boil forming.
- Hepar sulph - This is the most common treatment for boils, especially if the person is chilly and irritable. It is particularly helpful if the boil has moved into the stage where pus has formed. Hepar sulph is useful when there is a history of the skin being easily infected and slow to heal.
- Silica - When the boil is festering and produces a thin, clear discharge, silica can be helpful. This product can also be used on skin that is stubborn to heal and has a tendency to scar.
- Mercurius - When boils occur at the time of menstruation, mercurius can be used. The pus formation may be thin with a greenish tinge or if the boil is blood-tinged.
- Goldenseal - Take goldenseal in 500 mg capsule form. Goldenseal is helpful because of its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Topical treatments can include the bark of dogwood root, arnica, black walnut tree leaves, peppermint essential oil and ground flaxseed.
References
- Balch, J.F. & Stengler, M. (2004). Prescription for Natural Cures: a self-care guide for treating diseases and health problems with natural remedies including diet and nutrition, herbal medicine, nutritional supplements, bodywork, and more. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons Ltd
- De Vries, J. (1992). Skin diseases. Edinburgh : Mainstream
- Goodman, T. (1984).The skin doctor's skin doctoring book.New York : Sterling
- Papadopoulos, L. (2003). Understanding skin problems : acne, eczema, psoriasis and related conditions. Chichester, West Sussex : John Wiley and Sons Ltd
- Turkington, C., (1998). Skin deep : an A-Z of skin disorders, treatments and health. New York : Facts On File
Posted in Boils
Ask a Question Or Join a Discussion


